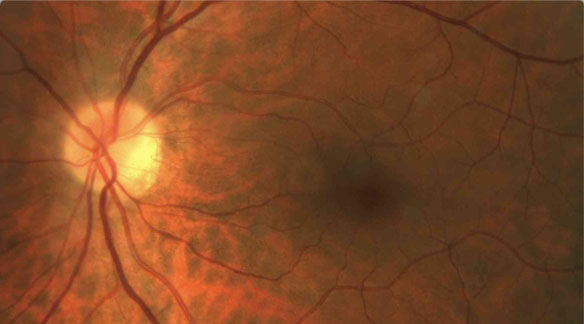
Digital Retinal PhotographyDigital retinal photography uses high-resolution imaging systems to capture images of the inside of your eye. This helps to assess the health of the retina and to detect and manage eye conditions and disease. Even the early signs of diabetic eye disease will be clearly visible with a retinal photo. The main structures that can be visualized on a digital retinal photo are
|  |
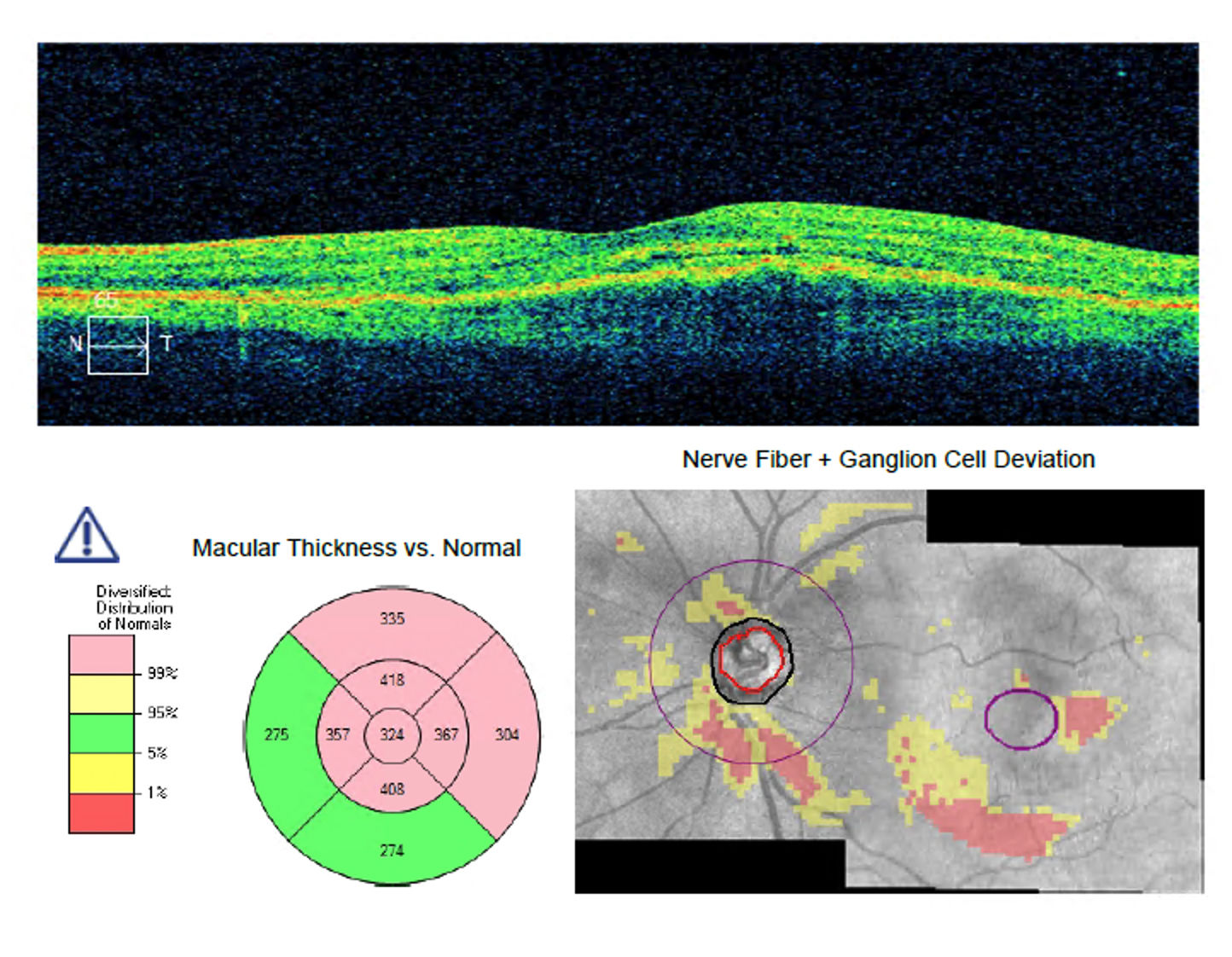 | Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina. With OCT, our ophthalmologist can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows our ophthalmologist to map and measure their thickness. These measurements help with diagnosis. They also provide treatment guidance for glaucoma and diseases of the retina. These retinal diseases include age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic eye disease. OCT is often used to evaluate disorders of the optic nerve as well. The OCT exam helps your ophthalmologist see changes to the fibres of the optic nerve. For example, it can detect changes caused by glaucoma. |
Wavefront Analysis – IOL calculationThe wavefront map is a complete, accurate description of all aberrations affecting your eye. Your eye doctor uses your wavefront map as a blueprint for custom-designing your vision correction, whether with refractive surgery such as LASIK, intraocular lenses, or glasses. Previously, with conventional methods of eye examinations, only lower-order vision errors could be diagnosed and treated. Higher-order aberrations such as spherical aberration were largely ignored by eye care professionals because their impact on vision was believed at the time to be slight and because no feasible means existed to precisely identify or correct them. Now that higher-order aberrations can be accurately defined by wavefront technology and corrected by new kinds of spectacles, contact lenses, intraocular lenses and refractive surgery, they have become more important factors in eye exams. Higher-order aberrations started receiving more attention because they were identified as sources of visual side effects after LASIK and other types of refractive surgery — causing halos, ghost images and other visual symptoms. Newer wavefront-guided lasers used in vision correction surgery can reduce certain higher-order aberrations, which may improve visual performance, especially for low-light activities such as driving at night. |  |
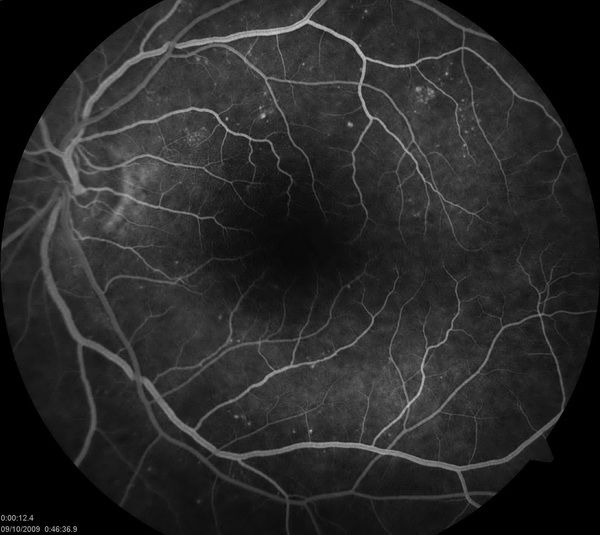 | Fluorescein AngiographyFluorescein Angiogram is used to determine if the blood vessels and other structures in the back of your eye are getting adequate blood flow by taking photos with a special camera. It is also used to track changes in eye disease over time and to target treatment areas. Fluorescein angiograms are used to find and diagnose eye diseases such as:
|
Humphrey Visual Field MachineA visual field test is a method of measuring an individual's entire scope of vision. Visual field testing maps the visual fields of each eye individually and can detect blind spots (scotomas) as well as more subtle areas of dim vision. The visual field machine is used to help in assessing whether a patient has glaucoma or visual loss for other reasons such as drug toxicity, a stroke or optic neuropathy. The test will be repeated on a regular basis to monitor and manage glaucoma. |  |

